A COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO THE MAJOR BUSINESS ANALYST DELIVERABLES?
Enroll today for CBAP - Business Analysis Certification Training now by clicking below.
The role of a business analyst is to manufacture a piece of art; the piece of art varies depending upon the methodology and techniques being used. Business analyst serves the project all through the beginning until the end and comes up with different pieces of art. It all depends on the case, the business analyst gets involved from the beginning of the project in the pre-sales, feasibility stage and goes further till the project ends into the operations and maintenance stage.
The artifacts created by business analysts go through different stages, and not all need to be presented to clients and stakeholders of the project. It is very essential to undertake all the principles and also considering the time while creating such items, and how they vary based on the project approach.
Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK) states about the two different forms of artifacts:
1. Work Product - A work product is a document where all the collection of notes and diagrams are used with the help of a business analyst all through the development process.
2. Deliverable - A deliverable is an exceptional and certifiable work product or service, where the party gives consent to delivery.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN WORK PRODUCT AND DELIVERABLE:
A business analyst must understand the difference between a work product and a deliverable. A work product states as a work in growth, unstructured and unsolved if shared with a stakeholder. A work product is used for gathering or shows the information and should not be taken as an absolute product for delivery until and unless proper structuring is done, with full information and evaluated.
For a business analyst, it’s not only the single work to do. His role has got so much to do as a business analyst encompasses few value-adding activities. Following are the categories that make sense as concerned with deliverables:
1. Understanding the Business
This is the first step for the job where you have to figure out where the business needs attention and to be solved. This is not particularly done by business analysts because you have to outline the returns on investment, giving a business a good reason and so on; for which business analyst needs to be prepared. It always varies from company to company, business analyst differs or refers to too many other identities and titles. My company, such as, calls it an IT Partner, normally partnering with a specific business segment such as marketing, sales, etc.
A business case as a High-Level Deliverable:
A business case is generally taken as an outcome of this, and it might take into account the output of different techniques that come together to illustrate that a problem needs a solution or there is an opening that takes an added advantage.
2. Planning Your Work
Once the decision has been made for a particular project; then it’s time to plan and decide as to how you will be doing the project as a business analyst. Planning is very essential and that too at initial stages because a business analyst can’t do the job all of his own. An analyst has to work out and outline the needs as to how they are going to work together with the stakeholders and acquire all the needs that need attention and the best possible solution that would work for them. Everybody’s involvement is required and they also make sure that all the resources such as people, tools, facilities, etc are provided as per the need. This step is meant to be very important as the contractor and statements of work will be required well on time.
Business Analysis Approach towards a plan should be High-Level Deliverable:
By the term high-level means that whatever comes out of this may be included in the planning of business analyst; as they might be broken down in small common deliverables such as work breakdown structure (WBS), communication plan, planning towards business analyst approach (Discussed below in detail) and necessity plans to manage.
Business Analyst Approach:
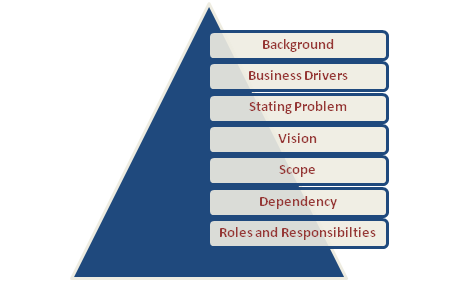
Following are the elements of the Business Analyst Approach:
- Background - States the purpose of the project and also provide background information.
- Business Drivers - This is the reason why the initiative is made with a purpose. Building up business needs at high levels that establish the reason for the project.
- Problem Statement - This statement states the reason for the project concerning the business term such as the importance required for new projects.
- Vision - Vision states the inspirational explanation as to what the company aims to achieve and accomplish.
- Scope - Focus on the boundaries that need changes.
- Dependency - Dependencies create a link, type of links, among all the tasks of the project and with other projects at the same time.
- Roles and Responsibilities - States the roles and responsibilities of the people performing the project.
3. Defining the Solution
This is the main role that people expect out of business analysis and especially what all deliverables are more or less required. Stating the solution is fundamentally required, as all solutions are required to meet the business needs and requirements, also called as requirement gathering.
Must have Documents- High-Level Deliverables:
This can vary with sizes and shapes; the main need in term of document it means that it should be a paper document but that’s not mandatory. By BABOK it is term as to be the “requirements package” that illustrates in a better way. This might comprise of traceability matrix, use cases, necessary solutions, meeting stakeholder needs, business compulsions and these can be in unusual forms such as diagrams, models or wireframes.
4. Evaluating the Solution
The solutions that are provided should be checked to evaluate and to meet business needs and requirements. This can be done in two ways:
a. When the required documents are done, solutions are intended and you are sure that your business needs are fulfilled.
b. When the required documents are done and you have to evaluate different possible solutions e.g. you want to buy a car and you make a list of cars you are interested in and you will see which car model works well for you instead of making your car.